
Why Every Business Needs an Information Security Policy
Data breaches are more common than ever. According to IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average cost of a data breach is $4.88 million, a 10% increase over the previous year.
Small businesses are especially vulnerable, with 43% of cyberattacks targeting them. Without a clear plan, your business could face financial losses, legal issues, and damaged trust.
Implementing a robust information security policy is the first step to safeguarding your business from these threats. Chris Butler, executive VP at IP Services says “An information security policy is a crucial tool that helps everyone in your organization understand how to keep sensitive data safe.”
This blog explains what information security policy is, why it’s essential, and how to create one. We’ll also provide a free information security policy template to get you started.
What is an Information Security Policy?
An information security policy is a set of rules and guidelines curated to protect your business’s sensitive data. It outlines how data should be handled, who can access it, and what steps to take in case of a breach.
This policy is not just for large corporations. Small businesses, too, need a clear plan to safeguard customer information, financial records, and intellectual property. Without one, you risk leaving your data exposed to cybercriminals.
Think of it as a roadmap. It helps your team understand their roles in keeping data safe and ensures compliance with laws like GDPR or HIPAA. A well-crafted policy reduces human errors that could lead to security incidents.
Key Components of an Information Security Policy
A strong information security policy covers several critical areas. Here’s what you need to include:
1. Scope and Objectives
Define what the policy covers and its goals. For example, it might protect customer data, employee records, or proprietary information.
The objectives should align with business priorities, such as protecting intellectual property or maintaining compliance with regulatory frameworks.
2. Roles and Responsibilities
Assign clear roles to team members. Who is responsible for monitoring security? Who handles breaches? Having clearly defined responsibilities prevents confusion during emergencies.
- IT administrators may oversee security monitoring.
- Employees must follow data handling policies.
- Executives should ensure compliance with security regulations.
3. Data Classification
Categorize data based on sensitivity. Not all data needs the same level of protection. Define categories such as:
- Public Data – Information that can be freely shared.
- Internal Use Only – Data for employees but not the public.
- Confidential Data – Sensitive business information requiring restricted access.
- Highly Confidential Data – Includes customer payment details, personal information, and trade secrets.
4. Access Control
Specify who can access what data. Limit access to only those who need it for their roles. Use role-based access controls (RBAC) to ensure employees only access data relevant to their responsibilities.
Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for additional security.
5. Incident Response
Outline clear steps to take during a breach. How should employees report an incident? Who should be notified? A strong incident response plan should include:
- Detection – Identifying a potential breach.
- Containment – Limiting the damage.
- Eradication – Removing the threat.
- Recovery – Restoring affected systems.
- Review – Learning from the incident to prevent future breaches.
6. Compliance Requirements
Ensure your policy aligns with industry regulations to protect your business from legal penalties. You must follow PCI DSS guidelines if your company processes credit card payments,. Healthcare organizations must comply with HIPAA regulations.
Why Your Business Needs an Information Security Policy
Cyberattacks are a growing threat. The FBI’s Internet Crime Report 2022 states that cybercrime complaints rose by 7% from the previous year, with losses exceeding $10.3 billion.
An information security policy helps you:
- Protect sensitive data from breaches.
- Build trust with clients and stakeholders.
- Avoid costly fines for non-compliance.
For SMBs, an information security policy template for small businesses can simplify the process. It ensures you don’t miss critical elements while saving time.
How to Create an Information Security Policy
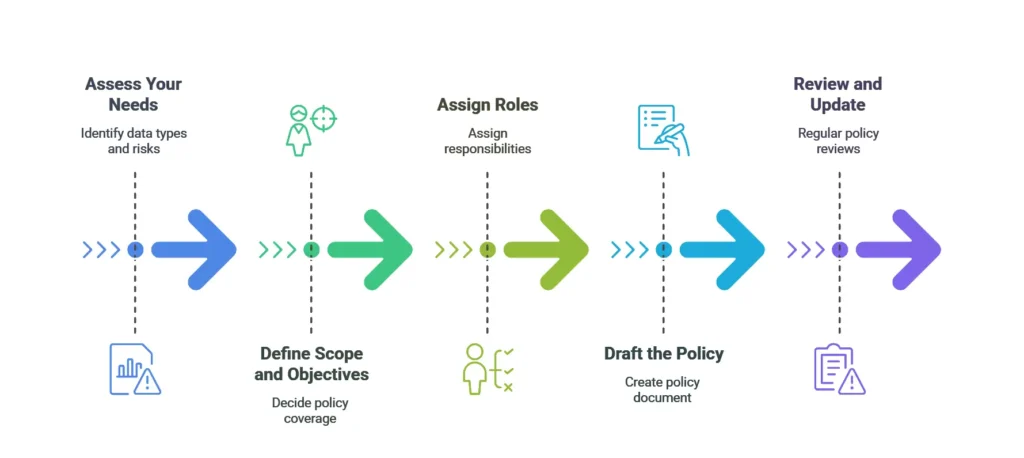
Creating a policy doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Follow these steps:
1. Assess Your Needs
Identify the types of data you handle and the risks they face. Do you store customer credit card information? Do employees use personal devices for work? Understanding these risks helps tailor your policy.
2. Define Scope and Objectives
Decide what your policy will cover. Will it focus on customer data, employee records, or both? Define what systems and networks fall under its protection.
3. Assign Roles
Clearly define who is responsible for implementing and maintaining the policy. Assign dedicated personnel for:
- Risk assessment
- Security awareness training
- Incident response coordination
4. Draft the Policy
Use a sample information security policy as a guide. Ensure it includes all key components, such as access control, password policies, and data encryption standards.
5. Review and Update
A policy isn’t static. Regularly review your policy to address new threats or changes in regulations. Annual reviews help ensure ongoing security improvements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid when Drafing an Information Security Policy
Many businesses make these errors when creating their policy:
- Overcomplicating the Document: Keep it simple. Your team should easily understand and follow the guidelines. Too much jargon can lead to confusion and non-compliance.
- Ignoring Stakeholder Input: Involve key team members in the process. IT teams, legal advisors, and department heads should all contribute to ensure the policy is comprehensive and practical.
- Neglecting Updates: Cyber threats evolve. Regularly update your policy to stay ahead. An outdated policy is as good as having no policy at all.
Key Regulations and Their Impact on Information Security Policies
Different industries face unique compliance requirements. Here’s a quick overview of key regulations and how they affect your information security policy:
| Regulation | Industry | Key Requirements | Impact on Policy |
| GDPR | All EU-based businesses | Protect personal data, report breaches within 72 hours | The policy must include data protection measures and breach response plans |
| HIPAA | Healthcare | Safeguard patient health information | The policy must address access control and encryption |
| PCI DSS | Retail | Secure payment card data | The policy must include secure data storage and transmission protocols |
| CCPA | California-based businesses | Allow consumers to opt out of data collection | The policy must outline data collection and consumer rights procedures |
Protect Your Business with IP Services’ Comprehensive Cybersecurity Solutions
An information security policy is critical for protecting your business from cyber threats. It ensures your team knows how to handle sensitive data, comply with regulations, and respond effectively to breaches.
IP Services specializes in cybersecurity solutions that help businesses like yours stay secure. From advanced penetration testing and incident response planning to compliance-as-a-service (CaaS), we provide the expertise and tools to safeguard your data and meet regulatory requirements.
Looking to strengthen your security? Contact us today to build a robust security framework for your business.


